Telemedicine Effectiveness for cardiovascular disease management
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for approximately 1.5 million deaths yearly. It is also the leading cause of disability, accounting for 675,000 Americans who can’t work or play like they used to. Telemedicine systems use technology such as video conferencing and medical equipment like blood pressure cuffs and heart rate monitors to deliver healthcare services remotely, improving access and care delivery while reducing costs.
The heart disease management mentioned in this blog covers heart attack detection using telemedicine systems, telemedicine advantages, and risk assessment for heart disease.
Table of Contents
- What is cardiovascular disease?
- What are the symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
- Cardiovascular disease risk factors
- The most common method of monitoring cardiovascular disease treatment
- What are the protocols used in telemedicine?
- What are the most popular devices for monitoring purposes in telemedicine cardiology?
- Conclusion
What is cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a complex disease that can impact any part of the heart or blood vessel. It refers to different types of heart diseases, like coronary heart disease, cardiovascular system disorders, heart attack, peripheral artery disease, and heart failure.
CVDs can be prevented or managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery. Another factor that can influence CVD risk is high blood pressure. High blood pressure means your blood pressure is higher than the normal range, and your risk of heart disease increases.
However, high blood pressure cannot be avoided altogether. Therefore, lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, eating healthy foods, and getting regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure levels.
What are the symptoms of cardiovascular disease?
Chest pain is the most common sign of cardiovascular disease. It can be caused by atherosclerosis or coronary artery disease.
Chest pain may also be associated with angina pectoris, a complication of heart disease in which chest pain occurs regularly and is accompanied by high blood pressure and pain in the heart muscle.
Shortness of breath is another symptom of cardiovascular disease. It can be caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or congestive heart failure.
Other symptoms include fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. Finally, angina pectoris is a symptom of a heart attack that occurs when coronary arteries become blocked due to atherosclerosis or coronary artery disease. This causes chest pain that can lead to death if treated quickly.
Telemedicine effectively treats cardiovascular disease patients with hypertension, high cholesterol levels, diabetes mellitus, obesity, smoking cessation, and diet modification programs.
Cardiovascular disease risk factors
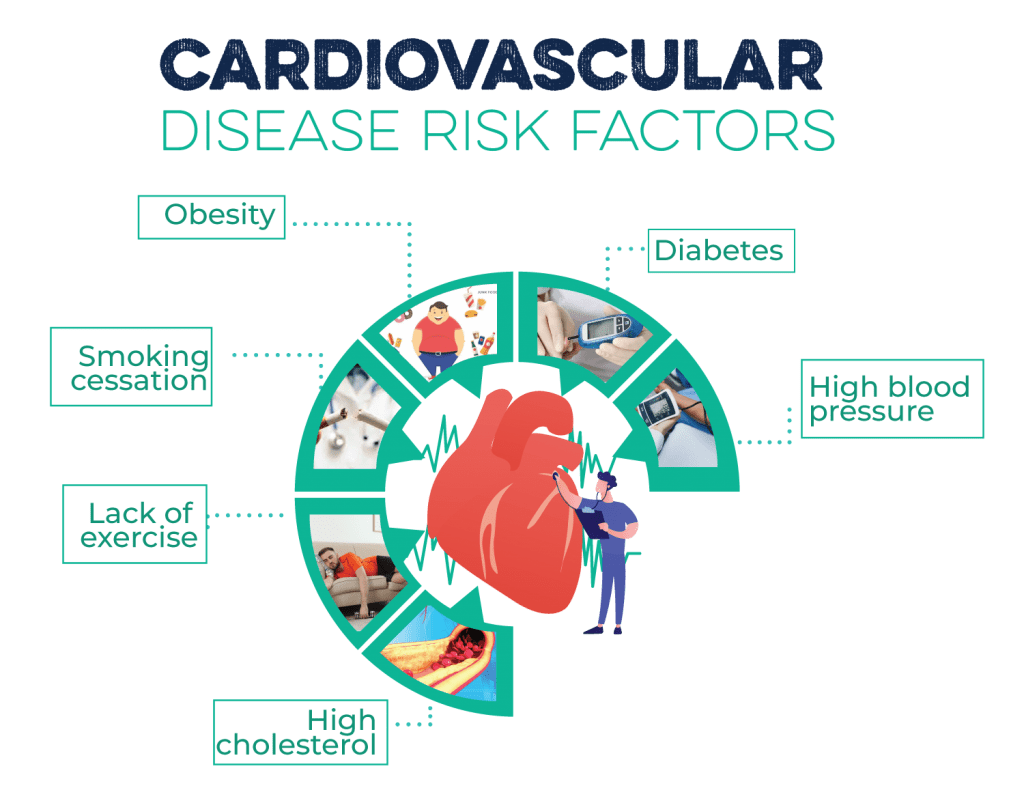
- Diabetes: uncontrolled diabetes is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. High blood pressure and obesity are also risk factors for cardiovascular disease. In addition, smoking, lack of exercise, and high blood sugar levels increase your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- High blood pressure: high blood pressure is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Hypertension can cause heart attack, stroke, or death from heart disease. Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking and reducing dietary cholesterol can help lower blood pressure levels.
- Obesity: obesity increases your risk of developing cardiovascular disease by raising your risk of hypertension, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes. Obesity also raises your risk of joint pain and arthritis, which may lead to heart failure or death from cardiovascular disease.
- Smoking cessation: smokers who quit smoking typically have a lower incidence of heart attack, stroke, angina, heart failure, and death from cardiovascular disease.
- Diet: diet can also affect your risk of developing cardiovascular disease. High blood pressure is most common in people with high blood sugar levels, low HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol), and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Lack of exercise: A sedentary lifestyle increases your risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Avoid smoking, lose weight if overweight, and exercise regularly to reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- High cholesterol: High cholesterol is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. The higher your blood cholesterol level, the greater your risk of heart disease.
The most common method of monitoring cardiovascular disease treatment
Home health care professionals provide round-the-clock monitoring of cardiovascular disease patients. In addition, patients can receive healthcare services through telemedicine, including visits from physicians via online video calls or remote medical monitoring.
Patients may also use telemonitoring to remotely monitor their vital signs and other health information by a team of physicians. Finally, patients can use teleradiology to have medical images and records transmitted over the internet for analysis by a physician. These technologies enable patients to receive care from a team of physicians anywhere, providing better access to high-quality care.
In addition, they provide an easy way for healthcare providers and patients to connect and coordinate care, leading to better outcomes for cardiovascular disease patients.
What are the protocols used in telemedicine?
The use of telemedicine in cardiovascular disease management effectively reduces the risk of complications and health care costs. In addition, it allows for high-quality care to be provided at a distance with minimal effort, leading to improved lifestyle outcomes and reduced burden on providers.
To use telemedicine in cardiac disease management, a clinician conducts a video conference with the patient. The clinician reviews the patient’s health history, assesses his or her current condition, and recommends treatment as needed.
These interventions can include blood pressure checks, electrocardiograms (ECGs), cardiac scans, or other tests necessary to provide high-quality care. The patient is then instructed to closely follow up with the clinician to ensure optimal care and outcomes.
Second, electronic health records cannot be shared between providers using telemedicine; this poses challenges when coordinating care between different physicians or hospitals. But these are only some of the limitations of using telemedicine; nonetheless, it is an effective healthcare tool that healthcare providers and patients should explore.
Connect with us to grow your revenue with telehealth technology
What are the most popular devices for monitoring purposes in telemedicine cardiology?
Many devices can be used for cardiac disease management in telemedicine. For example, ECG machines, blood pressure cuffs, heart rate sensors, and pulmonary function systems are all commonly used to monitor heart health in patients.
Using these monitors directly on a patient’s computer or phone makes it easy to ensure they receive high-quality care without traveling to see a doctor.
Heart rate monitors and blood pressure cuffs can measure blood pressure at any time without interfering with daily activities. In addition, patient monitors are also widely used for remote monitoring of vital signs. These devices are multifunctional healthcare tools that can remotely measure temperature, pulse rate, and other vital sign parameters.
E-health systems allow doctors to access vast amounts of health information from different sources and make informed decisions about care for their patients.
Telemedicine software provides a platform for physicians to remotely manage patient care by providing them access to healthcare information, medical records, and medical devices remotely from any Internet-connected computer or mobile device.
Finally, telemedicine services allow patients to access medical professionals through video conferences or telephone calls without traveling long distances. The use of these devices ensures patients can receive high-quality care regardless of their location or condition.
Conclusion
With telemedicine, healthcare professionals and patients can consult with trained specialists to monitor heart disease activity and changes in blood pressure, heart rate, blood vessel pressure, and chest pain.
Telemedicine benefits include improving treatment outcomes while reducing costs and travel time. In addition, the use of telemedicine has been shown to improve heart disease management.
Further research is needed to validate these findings. To learn more about heart disease risk factors and monitoring, check out our blog on ‘Heart disease risk factors explained by a cardiologist’ here.




